课时1
intro
这是一个课堂笔记,记录了某武汉大学计算机系本科生学习计算机组成和设计课程。
每次blog包含当日课时的知识点,以及对课后作业典型题的一个讲解析。
课程介绍
本课程的学习将使学生理解单处理器计算机系统中各部 件的内部工作原理、组成结构以及相互连接方式,具有 完整的计算机系统的整机概念;
理解计算机系统层次化结构概念,熟悉硬件与软件之间 的界面,掌握以MIPS为代表的RISC指令集体系结构的 基本知识;
能够对有关计算机硬件系统中的理论和实际问题进行计 算与分析;能根据指令语义进行单周期/多周期/流水线 数据通路及其控制器的简单设计;能对MIPS汇编程序设 计语言的相关问题进行分析。
教材: 计算机组成与设计:硬件/软件接口 David A.Patterson and John L.Hennessy, 第5版。
前导课程: 数字逻辑
C语言程序设计
考核方式
课后作业 20% 课堂随机点名 10% 期末考试 70%
计算机的种类
- PC,广泛的用途,性价比
- 服务器计算机,网络,高容量capcity,性能performance,稳定reliability
- 超级计算机,
- 嵌入式计算机,系统的一部分,有约束的电源,性能,耗费
十进制和二进制下的值和称呼
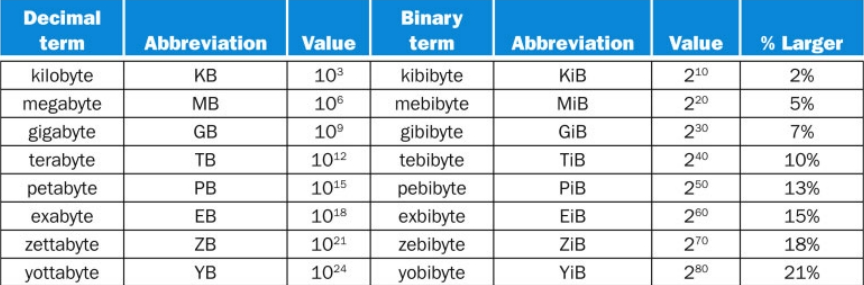
其他重要换算
1 GHz = Hz
1 ns = s
计算机的组建(冯诺依曼 )与发展
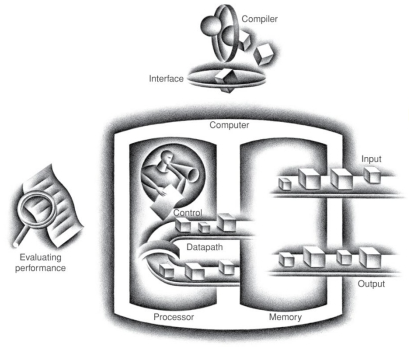
Same components for all kinds of computer
- Desktop, server, embedded
- Input/output includes User-interface devices
- Display, keyboard, mouse Storage devices
- Hard disk, CD/DVD, flash Network adapters
For communicating with other computers
半导体科技
从晶锭Silicon ingot到芯片
response time and throughout
response time:响应时间。How long it takes to do a task
throuughout: 吞吐量。Total work done per unit time
e.g., tasks/transactions/… per hour
一些值的定义和计算
performance
定义定义
倍数关系
X is n time faster than Y
eg:time taken to run a program:
10s on A and 15s on B
Thus, A is 1.5 times faster than B
measuring execution time
- Elapsed time
- Total response time, including all aspects
- Processing, I/O, OS overhead, idle time
- Determines system performance
- Total response time, including all aspects
- CPU time
- Time spent processing a given job
- Discounts I/O time, other jobs’ shares
- Comprises user CPU time and system CPU time
- Different programs are affected differently by CPU and system performance
- Time spent processing a given job
CPU Clocking
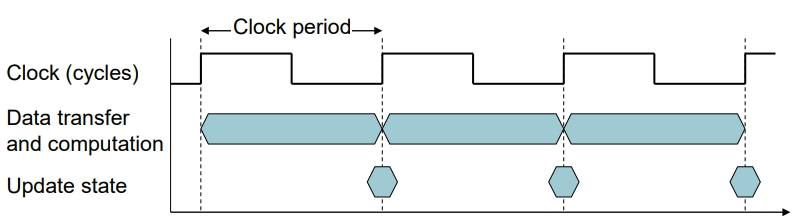
时钟周期时间Clock Period
ClockPeriod versus ClockCycle
Both the terms can generally be used for the same meaning however there might be a slight difference in the context of where it is used.
Consider the clock of the cpu which provides timing signals to coordinate all hardware, then while referring to the time interval of the clock after which it takes a transition is called its clock period. This is in general for any clock which provides a timing signal and is not restricted to only clocks providing timing signals to a cpu.(Think of the wall clock, the period of its second hand is 60 seconds)
And when we talk in terms of cpu architecture (like pipelining concepts), we use the term clock cycles to denote the time taken to complete 1 instruction(or 1 microinstruction). It kind of provides a layer of abstraction from the working of the clock(If lets say you change the clock, its clock period might change, but still in cpu terms we would still refer to it as 1 clock cycle).
个人理解上看,前者是一个具体的数值,比如这个CPU的clockperiod是1ns。后者是一个量词,比如这条指令耗费3个clockcycle。
另外,ClockPeriod也可称为clock cycle time, 简写为
时钟频率Clock Frequency
计算式
时钟周期时间Clock Period
时钟频率Clock Frequency
可以通过以下方式提高性能:
- 减少时钟周期的数量
- 提高时钟频率
- 硬件工程师经常需要权衡时钟频率和周期数量
Instruction Count and CPI
CPI: cycles per instruction。每个指令所需要的时钟周期。
IC: 这里笔者用作指令数量的缩写,而不是一般认为的集成芯片
指令数量。
Clock Cycles = IC CPI
More about CPI
Average and weighed average
提升性能
Detailed formula
Performance depends on :
- Algorithm: affects IC, possibly CPI
- Programming language: affectss = IC * CPI
CPU Time = IC, * CPI - Compiler: affects IC, CPI
- Instruction set architecture: affects IC, CPI, T
Power trend power wall multiprocesser
SPEC(Standard Performance Evaluation Corp)
SPEC CPU基准测试程序
SPECration 用来归纳12种整数基准程序(benchmark)的单一的数字
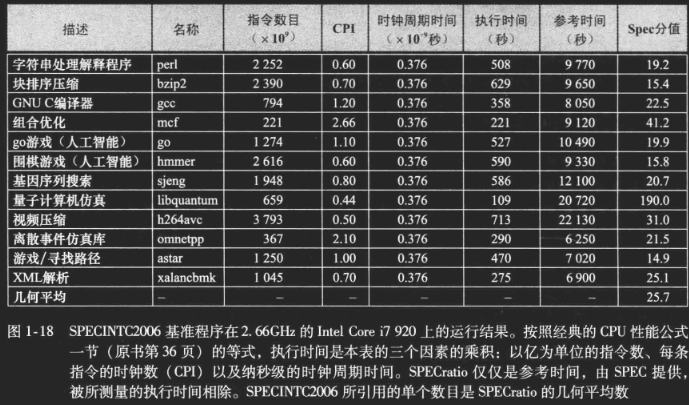
为了简化测试结果,SPEC 决定使用单一的数字来归纳所有 12 种整数基准程序。具体方法
是将被测计算机的执行时间标准化,即将被测计算机的执行时间除以一个参考处理器的执行时。SPECratio 值越大,表示性能越快 (因为 SPECratio 是执行时间的
间,结果称为 SPECratio
CINT2006或 CFP2006 的综合测试结果是取 SPECratio 的几何平均值。
逆天翻译,根据插图和相关题目的结果推测,
因此有,SPECratio 值越大,表示性能越快
几何平均值的公式是
其中,执行时间比 是总共 n个工作负载中第个程序的执行时间按参照计算机进行标准化的
结果。
SPEC功耗基准测试程序
性能采用吞吐率来测量,单位是每秒完成的操作次数。还是为了简化结果,SPEC 采用单个的数字来进
行归纳,称为“overall ssj_ops per watt”,其计算公式是:
式中,ssj_ops为工作负载在每10%增量处的性能,power 是对应的功耗。
Concluding Remark
Cost/performance is improving
- Due to underlying technology development
Hierarchical layers of abstraction
- In both hardware and software
Instruction set architecture
- The hardware/software interface
Execution time: the best performance measure
Power is a limiting factor
- Use parallelism to improve performance
例题
[时钟周期相关计算]
同一个指令系统体系结构有两种不同的实现方式。根据 CPI的同将指令分成四类(A、B、C和D)。P1的时钟频率为 2.5GHz,CPI分别为1、2、3和3;P2时钟频率为3GHz,CPI分别为2、2、2和2。
给定一个程序,有 1.0x10条动态指令,按如下比例分为4类: A,10%;B,20%; C,50%:D,20%。
a每种实现方式下的整体CPI是多少?
b.计算两种情况下的时钟周期总数。

额外的话,这道题的时钟周期总数只需要求ClockCycle的数量,所以就不需要用到Clockrate来求CPUtime了
spec分值相关
1.11 SPECCPU2006的bzip2基准程序在AMD Barcelona处理器上执行的总指令数为执
行时间为750s,参考时间为9650s。
1.11.1[5]<1.6,1.9>如果时钟周期时间为0.333ns,求CPI值。
[5]<1.9>求SPEC的分值。
[5]<1.6,19>如果基准程序的指令数增加10%,CPI不变求CPU时间增加多少?
[5]<1.6,1.9>如果基准程序的指令数增加10%,CPI增加5%,求CPU 时间增加多少?
[5]<1.6,19>根据上题中指令数和CPI的变化,求SPEC分值的变化。
[10]<16>假设开发了一款新的AMD Barcelona处理器,其工作频率为4GHz在其指令集中
增加了一些新的指令,从而使程序中指令数目减少了 15%,程序的执行时间减少到了 700.
新的CPI分值为13.7,求新的CPI。
[10]<1.6>当时钟频率由3GHz上升到4GHz时,上一小题算出的 CPI比1.11.1的高。请确
定CPI的升高是否与频率升高相同?如果不同,为什么?
[5]<1.6>CPU时间减少了多少?
[10]<1.6>对第二个基准程序 libquantum,假定执行时间为960ns,CPI为1.61,时钟频率为
3CHz。在时钟频率为4GHz时,在不影响 CPI的前提下执行时间降低10%,求指数
[10]<1.6>在指令数和CPI保持不变的前提下,如果要将 CPU 时间进一步减少10%,求时钟
频率。
10]<1.6>在指令数保持不变的前提下,如果要将 CPI降低15%,CPU 时间减少20%,求时
钟频率。




加速比的计算公式通常是:
回复删除$$
\text{加速比} = \frac{\text{优化前的执行时间}}{\text{优化后的执行时间}}
$$
举个例子,如果一个程序未优化时运行需要 10 秒,优化后只需要 2 秒,那么加速比就是 $\frac{10}{2} = 5$。这意味着优化后的程序运行速度是原来的 5 倍。